
The Small and Large Intestines · Anatomy and Physiology
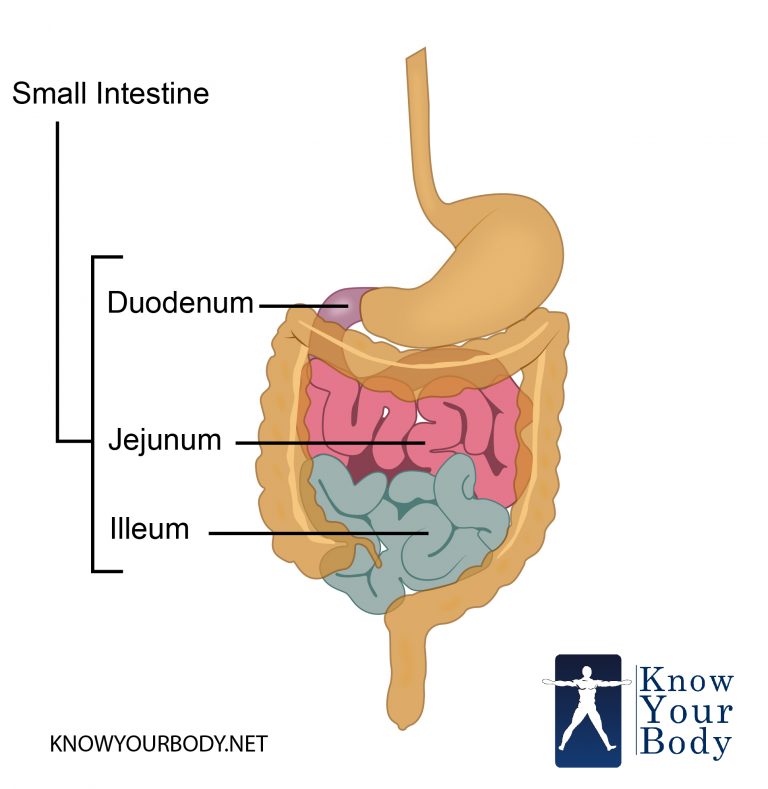
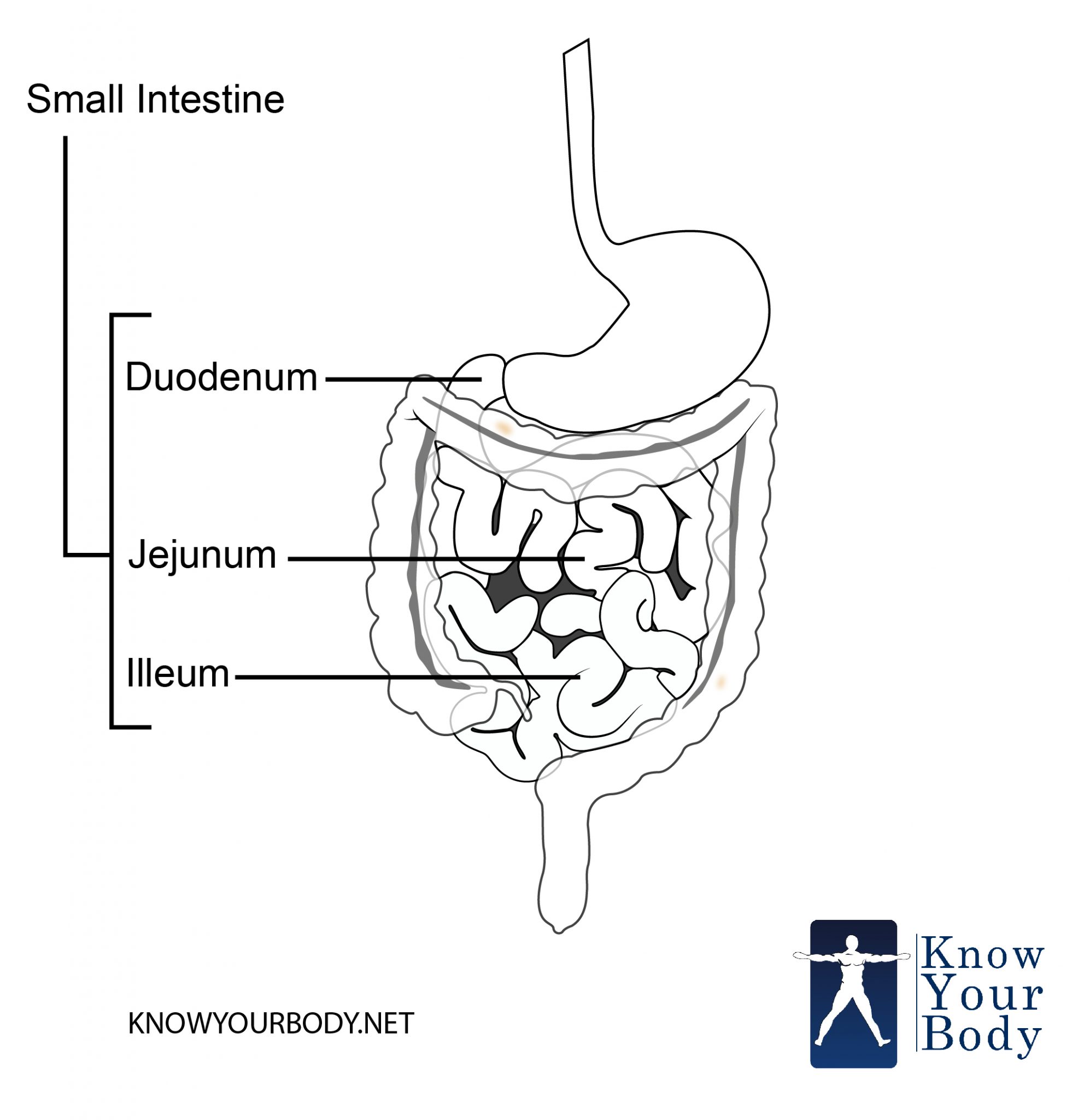
The small intestine has three distinct regions - the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.. The primary function of the small intestine is the absorption of nutri.

CCC Online Biology Lab small intestine histology model labeled and
The small intestine is part of your digestive system. It makes up part of the long pathway that food takes through your body, called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. When food leaves your stomach, it enters the small intestine, also called the small bowel. The small bowel connects to the large bowel, also called the large intestine or colon.

The Small Intestine Complete Anatomy
Summary The small intestine is a long-narrow tube that is part of the digestive system, found between the stomach and the large intestine. It is the primary site of nutrient absorption, where the majority of the breakdown and absorption of food occurs.

Small Intestine Location, Function, Length and Parts of the Small Intestine
The small intestine is made up of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Together with the esophagus, large intestine, and the stomach, it forms the gastrointestinal tract. In living humans, the.

Abdominal Cavity (no liver, stomach, small intestine) model STEM
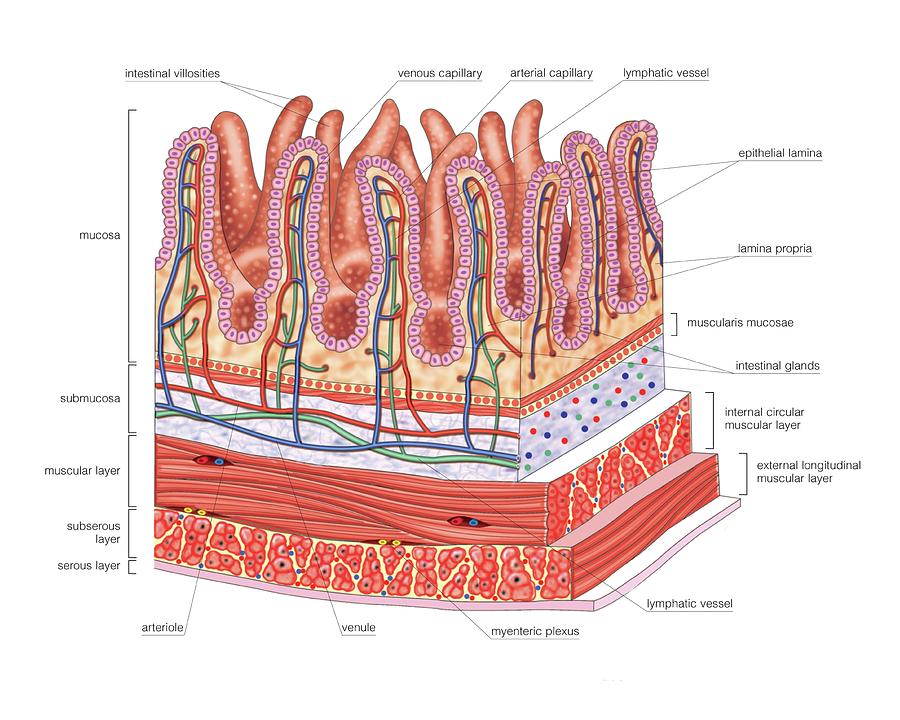
The Small Intestine's Layers. Section of duodenum: This image shows the layers of the duodenum: the serosa, muscularis, submucosa, and mucosa. The small intestine has four tissue layers: The serosa is the outermost layer of the intestine. The serosa is a smooth membrane consisting of a thin layer of cells that secrete serous fluid, and a thin.

small intestine histology labeled lab practical pics Human anatomy
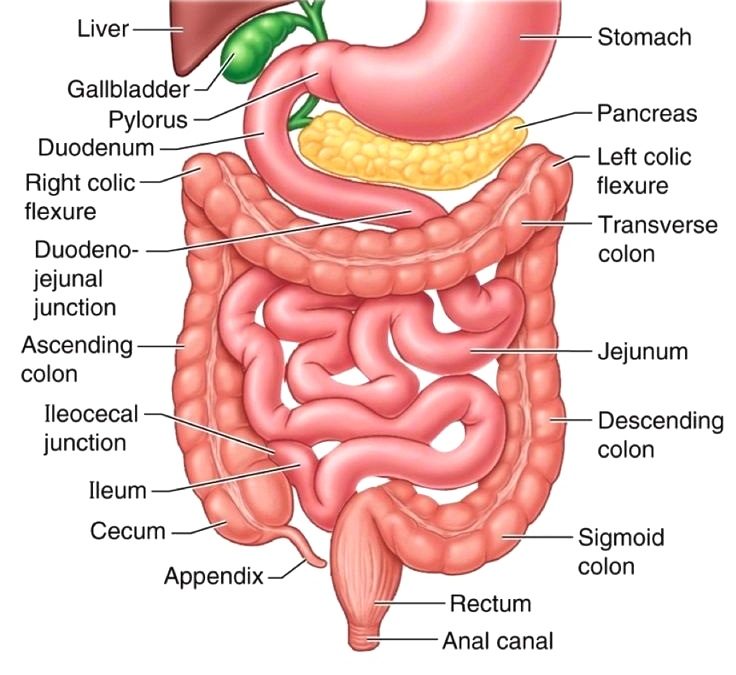
The digestive system. Diseases or Conditions Digestive Diseases File Size 361 KB | 1380 x 1716 File Type JPG The digestive system with sections labeled: mouth, esophagus, liver, stomach, gallbladder, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
Small Intestine Photograph by Asklepios Medical Atlas Pixels
This video was produced to help students of human anatomy at Modesto Junior College study our anatomical models.

small intestine villi model Google Search
marinamedicine. Accounting Final (Elliot) CHAPTER 1 - 8. 28 terms. ethanwillis24. 1 / 4. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum and more.

small intestine histology labeled Buscar con Google Para Histo
The small intestine is an organ located within the gastrointestinal tract.It is approximately 6.5m in the average person and assists in the digestion and absorption of ingested food. It extends from the pylorus of the stomach to the ileocaecal junction, where it meets the large intestine at the ileocaecal valve.Anatomically, the small bowel can be divided into three parts: the duodenum.
Small Intestine Function, Anatomy, Location, Length and Diagram
Anatomy (Macroscopy) The small intestine is a specialized tubular structure within the abdominal cavity in continuity with the stomach proximally and the colon distally. The small bowel is about 6 m in the adult. Three subdivisions; "the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum"are defined and characterized by various anatomic relationships.

Small and large intestine labeled Large intestine, Anatomy, Colon
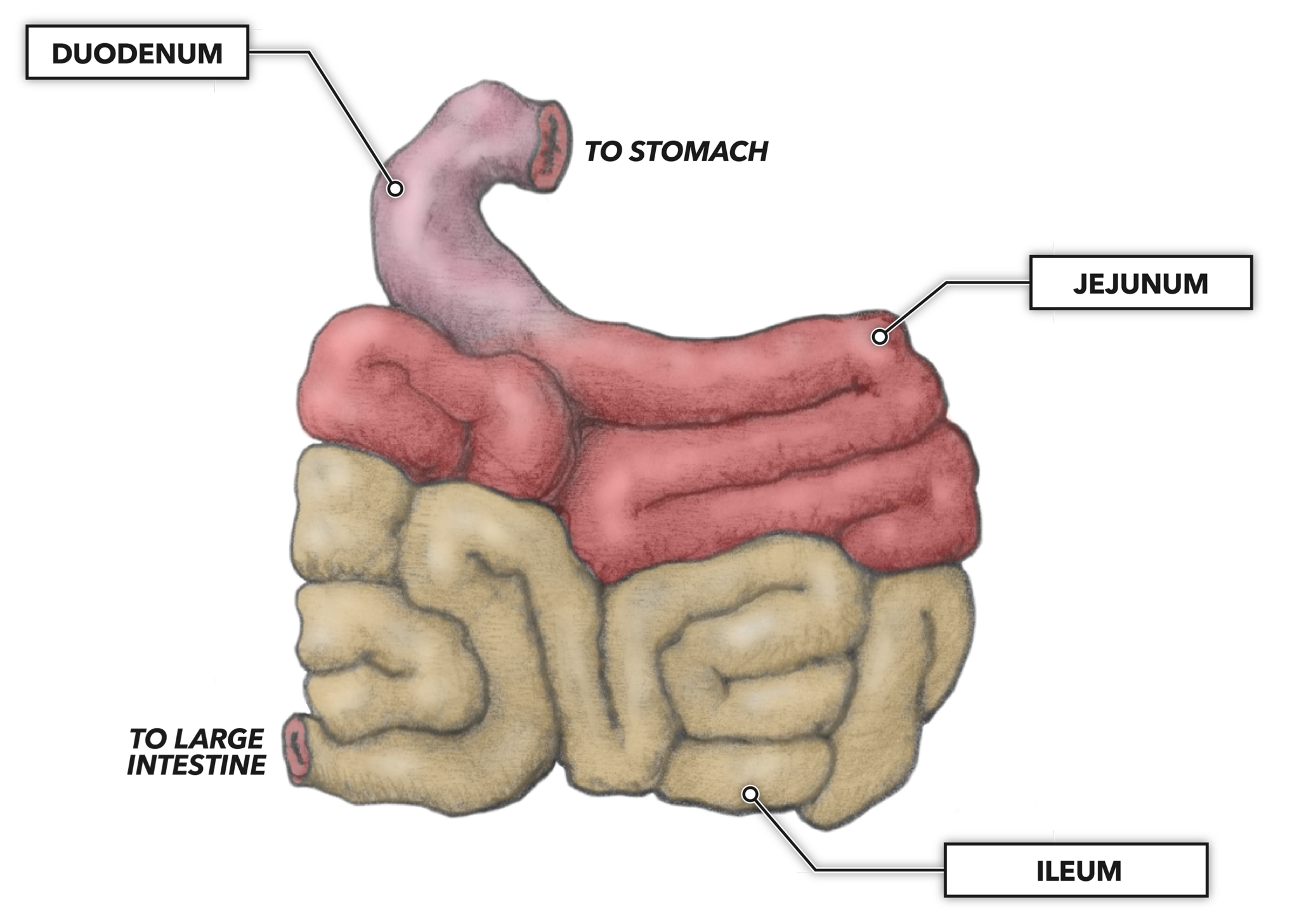
Structure The coiled tube of the small intestine is subdivided into three regions. From proximal (at the stomach) to distal, these are the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum ( Figure 23.18 ). The shortest region is the 25.4-cm (10-in) duodenum, which begins at the pyloric sphincter.

Image result for digestive system models labeled Digestive system
The small intestine is a crucial component of the digestive system that allows for the breakdown and absorption of important nutrients that permits the body to function at its peak performance. The small intestine accomplishes this via a complex network of blood vessels, nerves, and muscles that work together to achieve this task. It is a massive organ that has an average length of 3 to 5.
The Small Intestine Part 4 of the 5 Phases of Digestion
small intestine, a long, narrow, folded or coiled tube extending from the stomach to the large intestine; it is the region where most digestion and absorption of food takes place. It is about 6.7 to 7.6 metres (22 to 25 feet) long, highly convoluted, and contained in the central and lower abdominal cavity.
CrossFit The Gastrointestinal System Small Intestine
1/4 Synonyms: none The small intestine is the longest part of the digestive system. It extends from the stomach ( pylorus) to the large intestine ( cecum) and consists of three parts: duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The main functions of the small intestine are to complete digestion of food and to absorb nutrients.

small intestine villi model Google Search Label image, Anatomy
Absorption, Feces Formation, and Defecation. The small intestine absorbs about 90 percent of the water you ingest (either as liquid or within solid food). The large intestine absorbs most of the remaining water, a process that converts the liquid chyme residue into semisolid feces ("stool").
Small Intestine Function, Anatomy, Location, Length and Diagram
The mesentery of the small intestine is a large and broad fan-shaped mesentery that is attached to the jejunum and ileum of the small intestine, connecting them to the posterior abdominal wall. Superiorly, the mesentery of the small intestine is attached to the end of the duodenum/beginning of the jejunum (duodenojejunal junction) just to the left of the 2nd lumbar vertebra.